Limit of detection and quantitation
limit of detection (LOD):lowest possible analyte concentration that can be reliably detected using a specific analytical method. |
limit of quantitation (LOQ):lowest possible analyte concentration that can be reliably quantified using a specific analytical method. |
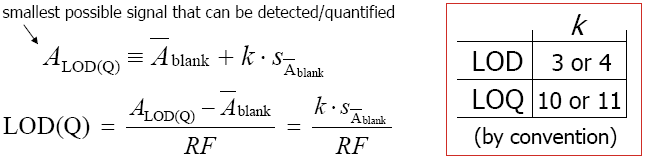
The lower LOD and LOQ, the better the analytical method
The analytical method can be improved by ...
(i) reducing the background noise (i.e., reducing)
... and/or ...
(ii) increasing the slope* RF of the regression curve
* the slope is also referred to as the sensitivity of the method; do not confuse sensitivity with the limit of detection LOD
Can you think of another criterion that describes the performance of an analytical method?



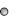 Limit of detection and quantitation
Limit of detection and quantitation