Matrix effects and ES calibration
matrix effect:
sample components suppress the response of the detector relative to 'clean' standards
example: signal suppression due to DOM (dissolved organic matter)
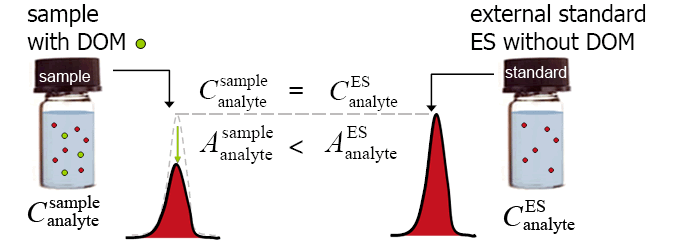
Signal suppression by matrix components in the sample results in quantified analyte concentrations in a sample that are systematically lower than the actual analyte concentrations in the sample.


 Matrix effects and ES calib.
Matrix effects and ES calib.
