Terminology
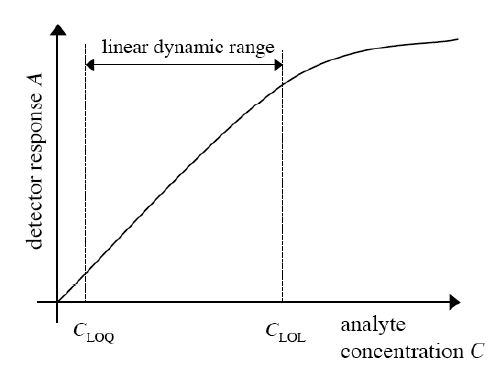
In the linear dynamic range , the response of a detector is linearly dependent on analyte concentration. Quantification should be performed in this range. Hence, the wider this range, the better.
Limit of linearity (LOL): analyte concentration above which the response of the detector departs from linearity. The higher LOL, the better.
Limit of quantitation (LOQ): lowest possible analyte concentration that can be reliably quantified using a specific analytical method. The lower LOQ, the better.
Limit of detection (LOD): lowest possible analyte concentration that can be reliably detected using a specific analytical method (note: LOD < LOQ). The lower LOD, the better.
Selectivity is defined as the extent to which a detection method can determine a particular analyte without interferences from other chemicals, analytes, or matrix components. The higher, the better for analyte identification.







 Terminology
Terminology