Sample contamination
Contamination of the sample by an extraneous source of the analyte.
For example, analyte molecules on the sampling equipment or the storing containers leach into the sample.
Two analyte classes for which there is a high risk of contamination:
1. Plasticizers (often phthalates)These are chemical additives widely used to soften plastic materials. Plastic sampling equipment and storage containers should be avoided when analyzing for plasticizers. |
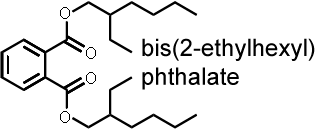 |
2. Detergents (either cationic, anionic, nonionic, or ampholytic)Water-soluble, surface-active chemicals (comprising a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic moiety) that are used for cleaning and degreasing. Contamination is likely if the sampling equipment and storage containers are cleaned with these chemicals prior to their use. |
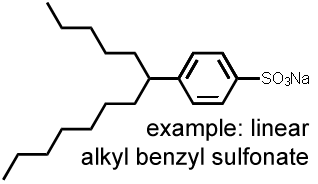 |

 Sample contamination
Sample contamination