General description of filter techniques
Principle:
- Sorption of analyte(s) from air A to sorbent material P in the filter: volumes up to several hundred m3 air are sucked through one filter by high volume sampler
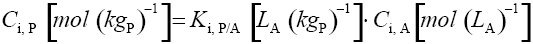
Note: This is an expression for partition equilibrium (note: non-equilibrium conditions prevail if flow rates are too high to allow attainment of local equilibrium for analyte(s) between the air and the sorbent phases)
- Thermal desorption of analyte from sorbent in an oven coupled to a GC system
advantage: simultaneous sampling and extraction |
disadvantage:potential breakthrough of analyte through filter |