General description of SPE
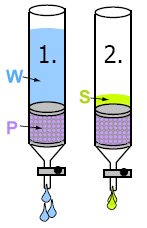 |
principle: 1. phase transfer of analyte from aqueous sample W (large volume) to sorbent P; 2. Elution of analyte from sorbent P in small volume of organic solvent S |
advantages:
|
disadvantages:
|
|
General description of SPE
|