3) Assign partition constants to substances
This table provides logarithmic partition constants log K iem> air/octanol
with K i air/octanol = C i air /C i octanol ) of the substances i = 2-Hexanone, n-Hexane, 1-Heptanol, 1-Hexanol, between air and the solvent octanol.
|
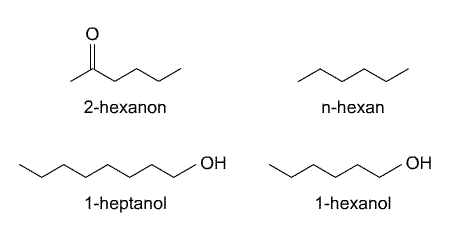 |
Assign the partition constants to the substances and explain shortly what made you choose this particular substance.
Answer: Hexane should have the least tendency to partition from air to octanol because it is the smallest of all compounds (see Rule 8) and does not form H-bonds with octanol ( log Kiao = -2.1); heptanol should have the largest tendency to partition from air to octanol because it is the largest of all compounds (see Rule 8) and it does form H-bonds with octanol as a H-bond acceptor and H-bond donor ( log Kiao = -5.8). Assignment of the remaining compounds should be self evident.
Download this page as a pdf