Lotus effect: self-cleaning surface
Imagine you would want to manufacture a surface from which any kind of dirt could be washed of with pure (rain) water.
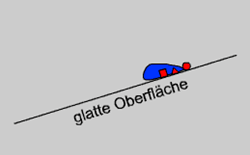
Of course, there is no problem to wash off water-soluble compounds, but greasy and oily particles rather attach to all kinds of surfaces instead of being washed off by water. Now, the first step obviously is to choose a material that has the least possible interactions with any kind of other materials (as there is no material that would repel other non-charged materials).
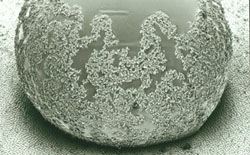
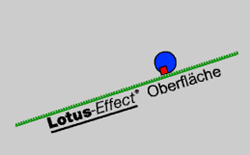
This material is TeflonTM. It exhibits no H-bond interactions and the smallest van der Waals interactions possible (that is why TeflonTM is used as surface coating in non-sticking pans). But this will not do yet. In fact, even water droplets readily adhere to TeflonTM. It appears that this problem only can be solved if one optimizes the phenomenon that has been the major challenge to the gecko, i.e. create a surface that is so rough (on a molecular level) that the dirt particles find only few contact points thus yielding very small van-der-Waals forces. As a consequence the particles will rather attach to a water droplet (with a smooth surface) even though they might not be able to interact via Hydrogen bonds. As a positive side effect the water droplets themselves will also readily run off from such a surface.
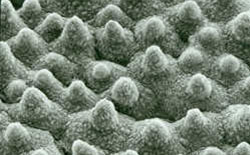
In the case of the lotus flower the surface material is wax not TeflonTM. Wax does exhibit slightly higher van der Waals forces than TeflonTM but just as TeflonTM it does not engage in H-bonding. Due to its optimal surface structure the plant does show this self-cleaning “Lotus”-effect . This effect has been studied in depth by Prof. Barthlott, Dr. Neinhuis and their group at University of Bonn, Germany and they have realized that this self-cleaning effect can be used to improve many articles of daily use (e.g. clothing, carpets, dishes and container a.s.o.). Typicallly, perfluorinated materials are used for this surface treatment because - just like TeflonTM - they exhibit no H-bonding and only weak van-der-Waals interactions.
 |
 |
Wax crystals on the surface of a lotus leaf
|
Water droplet with particles on its surface
|
 |
 |
Links:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrophobicity#Superhydrophobicity
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lotus_effect
http://www.lotus-effekt.de/
Download this page as a pdf


 Lotus effect
Lotus effect