Other remarks:
Be sure to read Box 1 in the script about the 'units of partition constants'. Reading the box will save you a lot of time (and frustration) when it comes to the calculations in chapter 3.
Here are two examples of costly mistakes due to wrong unit conversion: http://jittdl.physics.iupui.edu/jitt/sampler/chemistry/goodfors/goodformathskills.html and another one for problems with different reference systems: meereshoehe.pdf (in German).
Link to an unit conversion calculator: http://www.digitaldutch.com/unitconverter/
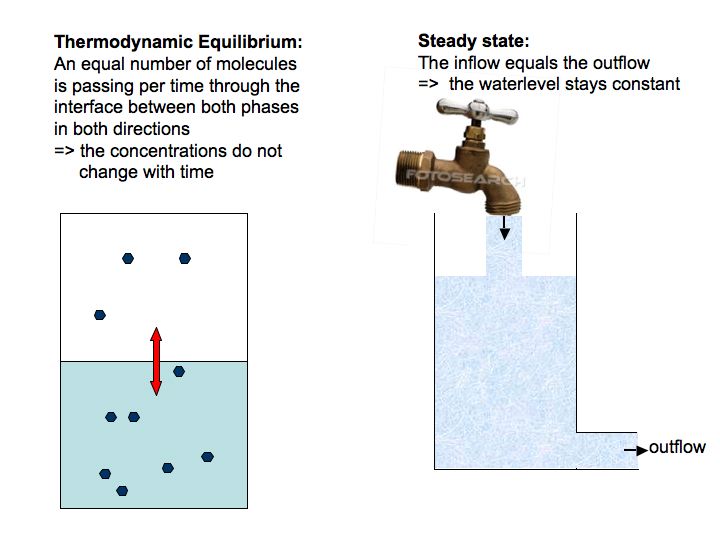
There is one more important thing you should be aware of: the difference between a thermodynamic equilibrium and a dynamic equilibrium! Both equilibria represent steady state conditions, i.e., there are no net changes in concentrations in each phase over time. However, whereas in thermodynamic equilibrium the system boundaries are closed, a dynamic equilibrium is characterized by open system boundaries across which the rate of outflow (or loss, consumption) equals the rate of inflow (or production).
Download this page as a pdf



 Other remarks
Other remarks