Chromatographic system - 2
Measuring retention factor Ri:
delay in elution from column relative to a non-sorbing tracer compound
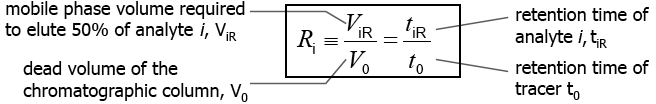
Calculating retention: Transport of analyte only in the mobile phase
e.g. if only 10% are in the mobile phase then R= 1/0.1 = 10
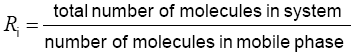
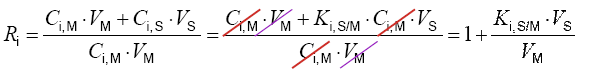
The partitioning constant of analyte between the mobile and the stationary phase may be changed during the course of a chromatographyc run.
Phase Ki, S/M can be altered during a chromatographic run by: