Sorption isotherm
Answer:The experiment will result in a linear relationship (i.e., constant slope of the curve) with zero as the ordinate intercept (Note that zero concentration in phase 1 must correspond to zero concentration in phase 2).
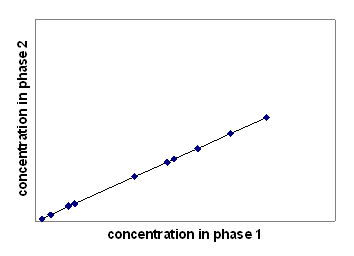
The partition constant is identical to the slope of this curve because K equals c*i 1 /c*i 2 .
If i was a volatile compound and the bottle also contained 1 L of air while the same amounts of i were added to the system like before, then the measured concentrations in phase 1 and 2 would be smaller than in the absence of air in the system. However, the data points would still lie on the same straight line as the one shown above.
Download this page as a pdf



 Answer
Answer